The IT industry is evolving rapidly with new automation trends focused on enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving business processes. One of the most advanced automation concepts driving this transformation is Hyperautomation. Let’s explore it in more detail.
- Definition: Hyperautomation extends beyond basic RPA by integrating multiple technologies like AI, machine learning (ML), process mining, and analytics to automate complex, end-to-end processes.
- Key Technologies: RPA, AI/ML, business process management (BPM), process discovery tools.
- Use Cases: Automating invoice processing, predictive analytics in customer service, and enhancing decision-making in supply chain management.
What is Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation refers to the concept of automating complex, end-to-end business processes by integrating advanced technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Business Process Management (BPM), and process mining. It aims to automate not only repetitive tasks but also decision-making and more complex, unstructured workflows, providing an organization-wide transformation. Gartner coined the term “hyperautomation” as the next evolution of automation, which focuses on automating every process possible and constantly optimizing workflows through data-driven insights.
Key Technologies Involved in Hyperautomation
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
RPA automates routine, rule-based tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and system interactions. It acts as a foundation for hyperautomation by taking over repetitive manual tasks that require no cognitive input. - Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI enhances automation by enabling systems to handle more complex tasks. Through natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and machine learning algorithms, AI can automate unstructured data tasks, make decisions, and learn over time. - Machine Learning (ML):
ML models within hyperautomation provide predictive analytics and can improve decision-making processes. For example, ML can analyze historical data to predict customer behaviors, optimize supply chains, or detect anomalies in financial transactions. - Process Mining:
Process mining tools analyze existing workflows to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where automation can be applied. By visualizing the actual execution of business processes, it helps optimize and re-engineer workflows. - Business Process Management (BPM):
BPM focuses on improving the efficiency of business processes. It works hand-in-hand with automation by managing and orchestrating complex workflows, ensuring that tasks are executed in the right order across different systems and people. - Low-Code/No-Code Platforms:
These platforms enable business users (citizen developers) to build and automate workflows with minimal coding. Low-code solutions empower teams to implement automation without needing a deep understanding of software development, thus accelerating automation deployment. - Optical Character Recognition (OCR):
OCR technology is used to digitize and extract text from scanned documents, PDFs, and images. In hyperautomation, OCR combined with AI enables the automation of document-heavy processes (e.g., extracting data from invoices or forms). - Intelligent Document Processing (IDP):
IDP automates the extraction, classification, and interpretation of data from various document types. It enables automation for unstructured and semi-structured data, using AI models to learn and improve over time. - Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP allows machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language. It is crucial for chatbots, voice assistants, and text-based automation tasks such as processing customer support tickets or interpreting emails. - Analytics and Data Science:
Data analytics and AI-driven insights are crucial to monitor and improve automated processes. Hyperautomation leverages analytics to measure the effectiveness of automation initiatives, forecast trends, and optimize operations.
The Lifecycle of Hyperautomation
- Process Identification:
- The first step in hyperautomation is identifying which processes to automate. Tools like process mining and task mining help analyze how business processes are currently being executed. They highlight inefficiencies and suggest processes ripe for automation.
- Key Goal: Prioritize high-volume, high-impact processes with potential for full automation.
- Process Optimization:
- Before automating, processes should be streamlined and optimized. This ensures that automating inefficient processes doesn’t lead to faster inefficiencies.
- Key Goal: Eliminate redundancies and standardize workflows to create a foundation for automation.
- Automation Implementation:
- Deploy RPA bots to handle repetitive, rules-based tasks. Then, augment the automation with AI/ML to enable decision-making, processing unstructured data, and handling exceptions.
- Key Goal: Use RPA for standard processes and AI for handling variability and cognitive tasks.
- Integration with BPM Tools:
- Use BPM tools to orchestrate automated processes across departments. This ensures that automated tasks fit into broader workflows, providing end-to-end automation.
- Key Goal: Achieve full process orchestration where RPA, AI, and human tasks work seamlessly together.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization:
- Hyperautomation is not a one-time implementation. Continuous monitoring through analytics and process mining helps identify bottlenecks or new areas for automation.
- Key Goal: Use real-time data to optimize automated workflows continually.
Key Benefits of Hyperautomation
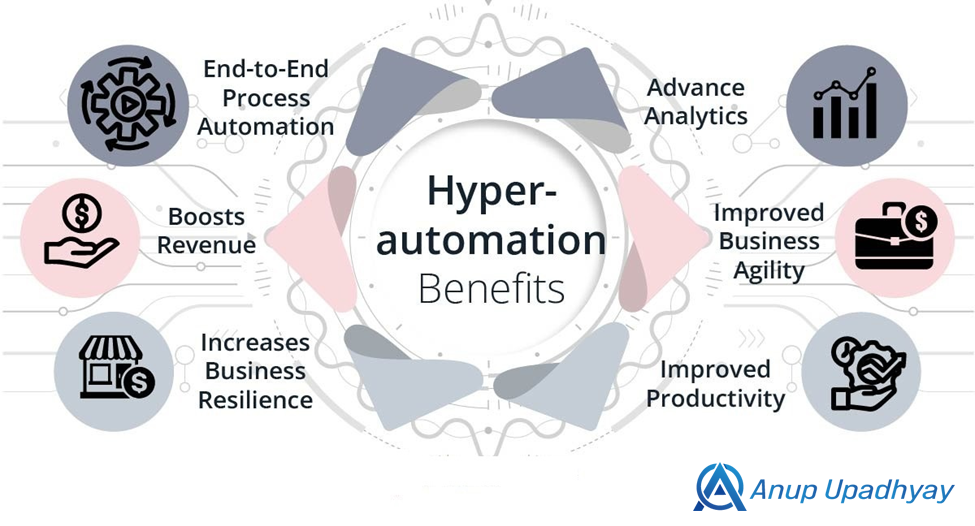
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity:
Hyperautomation eliminates manual, repetitive tasks, significantly improving process speed and accuracy. It allows organizations to achieve greater outputs with fewer resources. - Scalability:
Hyperautomation is designed to scale across an organization. As more processes are automated, and as AI and ML models become smarter, the automation framework can be scaled to new departments and functions without significant manual intervention. - Enhanced Decision-Making:
By leveraging AI/ML, hyperautomation allows businesses to make data-driven decisions. Predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, and automation of decision-heavy tasks enable faster and smarter decision-making. - Improved Compliance and Risk Management:
Automated processes are consistent, auditable, and can be programmed to follow strict compliance rules. This reduces human error and ensures compliance with regulatory frameworks (GDPR, ISO, etc.). - Cost Reduction:
Hyperautomation drives significant cost savings by reducing reliance on manual labor, increasing efficiency, and minimizing the risk of errors that could result in financial penalties or lost business opportunities. - Better Customer Experience:
With hyperautomation, businesses can offer faster, more personalized services. For example, AI-driven chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, while RPA can expedite order processing and service delivery. - Workforce Augmentation:
Hyperautomation doesn’t necessarily replace jobs but augments the workforce by allowing employees to focus on high-value, strategic work while bots and AI handle mundane, repetitive tasks. - Improves Team Collaboration
To make it easier for all the teams in an organization to collaborate, hyperautomation combines software bots, RPA, and other intelligent tools and lets all users interact across all the core processes of an organization. Hyperautomation involves everyone by connecting operations, processes, and data.
- Provides Agility in Business
Agility in business refers to how fast your business can adapt to changes as required and grow. Companies can be assured of scalability, which consists of hyperautomation technologies. Utilizing intelligent automated tools that are layered together makes it convenient for organizations to tap into new opportunities, change according to the dynamic nature of the market, and evolve as necessary.
- Offers Advanced Insights
Often, companies can’t figure out their inefficiencies and how they affect the organization. To improve their processes and optimize them for enhanced returns, the organization’s leaders need in-depth insights from the data, which they can achieve only after incorporating the capabilities of advanced analytics tools. Hyperautomation can help businesses by letting companies reach the potential of all their data and help them derive insights that will aid them in understanding current trends and making future predictions and refinements.
- Upgrades Data Storage and Accessibility
Performing seamless interactions across on-site infrastructure and data storage are achieved by hyperautomation by integrating different intelligent processes and software. As more companies adopt hybrid/multi-cloud infrastructures, the integration of hyperautomation processes has become significant for the transformation. It provides smooth communication across all systems and ensures that data can be accessed from centralized storage for all the core systems. Digital twins can be generated using machine learning and AI in hyperautomation, which are the virtual models of physical infrastructures or procedures.
Challenges of Hyperautomation

- Complexity in Integration:
- Integrating multiple technologies (RPA, AI, ML, BPM) into a seamless workflow can be complex and requires robust architecture and careful planning.
- Change Management:
- Hyperautomation can dramatically change the way work is done. Employees may resist automation due to fear of job loss or unfamiliarity with new tools. Managing this change is crucial for successful implementation.
- Data Quality:
- AI and ML models rely heavily on high-quality data. If the data feeding the automation process is incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated, it can lead to flawed decisions and automation failures.
- Governance and Security:
- Automation of processes, especially those involving sensitive data, requires strong governance frameworks to manage security, compliance, and ethical concerns.
- Cost of Implementation:
- While hyperautomation promises long-term ROI, the initial cost of implementation (tools, integration, training) can be significant. It’s important to have a clear roadmap to ensure cost-effective automation.
- Strategic Planning
- Even if business owners come with a technical background and understanding of how hyperautomation works and how it can affect their business performance, it becomes difficult to implement it strategically. For example, automating the entire process of a department will require businesses to incorporate an IT structure, reduce the number of staff and install all the required software applications. It needs to be integrated not to disturb the business performance but to enhance it.
- Trial and Error
- Just because an organization has implemented hyperautomation to its processes, it can’t just expect its business operations to achieve a great return on investment and efficiency. The company will need to try a trial-and-error method to figure out the best way it can achieve success. It will require meticulous planning, consistency, and strategy-making decisions. The benefits before and post-implementation of hyperautomation applications will need to be analyzed and measured by professionals to make the necessary changes.
- Automation wasn’t widely received when it was primarily introduced in different industries. Most companies were hesitant to adopt this new technology as they didn’t know much about it. As more people become familiar with hyperautomation benefits, the trend of incorporating it within their operations is increasing. Hyperautomation consists of several advanced and sophisticated technologies that help automate processes and provide efficiency. It is not just an advancement in technology but also a disciplined approach for businesses to streamline their operations by consuming minimal time, even with a high influx of demand.
Use Cases for Hyperautomation
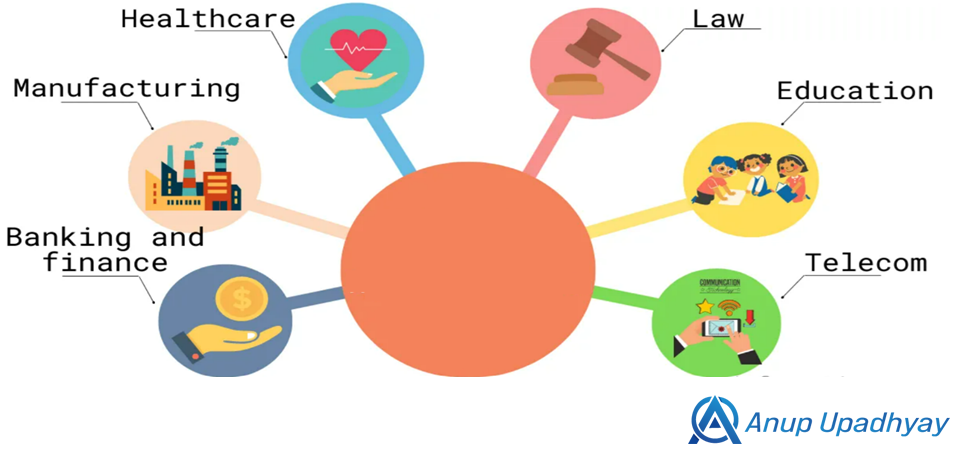
- Finance and Accounting:
- Automating end-to-end invoicing, financial reporting, tax compliance, and reconciliation processes.
- AI-driven fraud detection, credit scoring, and predictive financial analytics.
- Human Resources (HR):
- Automating employee onboarding, payroll, leave management, and performance reviews.
- Using AI to match job candidates to open positions and analyze employee satisfaction data.
- Healthcare:
- Automating patient data processing, insurance claims, and appointment scheduling.
- AI/ML models analyzing medical data for early diagnosis or treatment recommendations.
- Supply Chain Management:
- Automated inventory management, order processing, and vendor coordination.
- AI-driven demand forecasting and logistics optimization.
- Customer Service: Integrating AI-powered chatbots and RPA for 24/7 customer support, automated ticket resolution, and customer feedback analysis.
Future of Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation is expected to grow rapidly, with advancements in AI/ML and the increasing integration of IoT and edge computing. As organizations embrace a “digital-first” approach, hyperautomation will drive new levels of operational efficiency and innovation, enabling businesses to stay competitive in an increasingly automated world.
Key trends include:
- Increased Use of Cognitive Automation: More complex decision-making tasks will be automated, thanks to advancements in AI.
- Self-Healing Systems: Systems that detect issues and automatically trigger remediation actions without human intervention.
- Democratization of Automation: With low-code/no-code platforms, more business users (non-developers) will be able to automate their workflows.
In summary, hyperautomation is not just about automating processes but creating an intelligent, data-driven ecosystem that continuously learns and evolves, driving transformation across the enterprise.
Explore more on Future of HyperAutomation at https://anupupadhyay.com/future-of-hyperautomation-a-comprehensive-outlook/
Thanks


